Understanding Web 3: The Next Evolution of the Internet
The internet has undergone significant transformations since its inception, evolving from a static, one-way communication platform to the dynamic, interactive experience we know today. To fully grasp the concept of Web 3, it’s essential to understand how we got here, starting with Web 1.
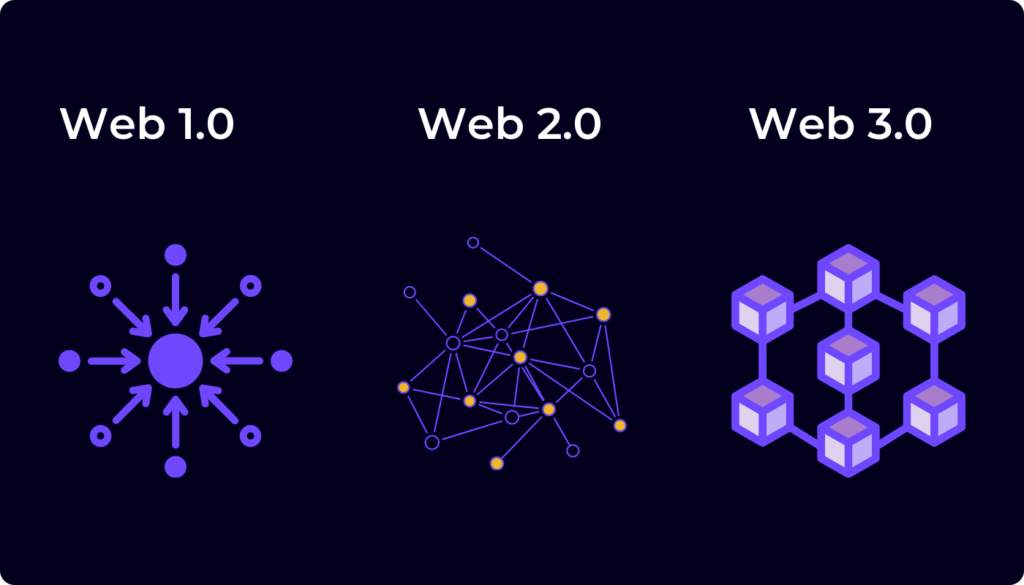
Web 1: The Birth of the Internet
The internet began evolving around 1960, but it wasn’t until 1993 that it became widely recognized, especially as businesses started using it to create websites. These websites allowed businesses to showcase their offerings to a global audience. During this era, known as Web 1, the internet was mostly a one-way street. Content creators, often business owners, had the power to display whatever they wanted, while users could only consume this content. Interaction was limited; you could read, but not contribute or interact with the content in any meaningful way.
Web 2: The Rise of Social Media and User-Generated Content
The launch of Facebook in 2004 marked the beginning of Web 2. Other platforms like YouTube (2005) and WhatsApp (2009) quickly followed, ushering in a new era of internet usage. Unlike Web 1, Web 2 allowed users not only to read content but also to create and share their own. Platforms like Facebook provided a free space for users to post content, share ideas, and interact with others. However, this freedom came at a cost.
While these platforms are free to use, the saying goes, “If you’re not paying for the product, then you are the product.” In Web 2, your data became the currency. Companies like Facebook and Google began to collect user data to monetize their platforms. This led to a loss of control over personal data, with tech giants having full authority over how this data was used. For example, if you frequently search for cars, you might notice that ads across various platforms start to target you with car-related content. This is because your data is being leveraged for profit, often without your explicit consent.
The Need for Web 3
The limitations of Web 2, particularly around data ownership and privacy, highlighted the need for a new, more user-centric version of the internet—enter Web 3.
Web 3: A Decentralized Future
Web 3 represents a significant shift from the current model. While services like Instagram, Facebook, YouTube, and Google will continue to exist, the key difference is in how they operate. Instead of relying on centralized servers, as is currently the case, Web 3 platforms will run on decentralized, peer-to-peer networks, specifically on blockchain networks. This transition will lead to the creation of decentralized applications (DApps), which offer numerous advantages over traditional platforms.
Key Advantages of Web 3
- Decentralization: Built on blockchain technology, Web 3 is decentralized, meaning no central authority controls the network. This decentralization fosters greater trust and transparency in online interactions.
- Data Ownership and Control: Users in Web 3 have greater control over their personal data, digital identities, and the content they create. They can choose what information to share and with whom, significantly reducing the power of tech giants over personal data.
- Improved Privacy: Web 3 enhances privacy through encryption and decentralized data storage, reducing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access to personal information.
- Smart Contracts: A key feature of Web 3, smart contracts automate and enforce agreements without intermediaries. This can streamline processes in industries such as finance and real estate.
- Immutable Data: Data stored on blockchain networks is tamper-resistant and cannot be easily altered or deleted. This is invaluable for maintaining a secure and auditable record of transactions and information.
- Incentives for Participation: Web 3 networks offer token-based incentives for users who participate in network activities, contributing to the network’s growth and sustainability.
- Reduced Fees: By eliminating intermediaries, Web 3 can reduce transaction costs and fees associated with various online activities.
- Censorship Resistance: Decentralized networks in Web 3 are less susceptible to censorship and government control, making it more challenging to suppress free speech and information.
- Empowerment: Web 3 empowers individuals by giving them more control over their online experiences, financial assets, and digital interactions. It reduces reliance on centralized authorities.
- Innovation: Web 3 has the potential to drive innovation across various industries, including finance, healthcare, and real estate, by providing tools and platforms for developers and entrepreneurs.
Conclusion
Web 3 is poised to revolutionize the way we interact with the internet. By addressing the limitations of Web 2, particularly around data ownership, privacy, and control, Web 3 offers a more secure, transparent, and user-centric online experience. As we move towards this decentralized future, the internet will become a space where individuals truly own their data and digital identities, paving the way for a more equitable and innovative digital world.
ENG WANJIKU
Views: 137