A hash is a unique identifier that distinguishes and identifies a particular txn in the crypto network. It a combination of a set of numbers and alphabets similar to bank txns or even Mpesa txns codes.
Hash ID will let you know whether a txn has occurred or not.
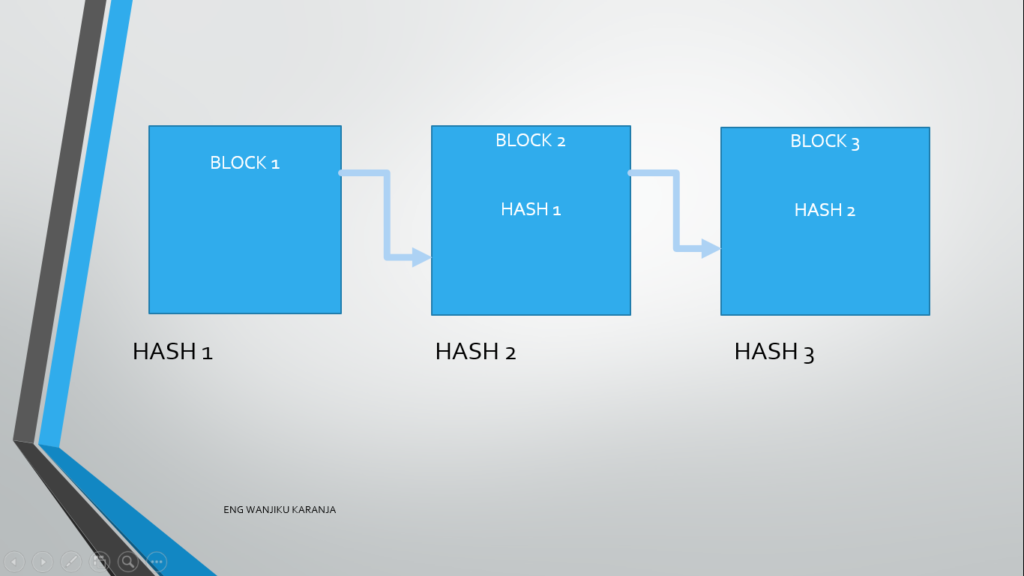
In this blocks the hash of the previous block is saved in the next block and so on. And that’s how we form a chain
•Who adds this blocks in this chain ?
•Who verifies this transactions ?
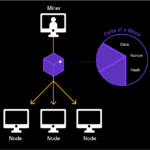
•In BTC txns ,the people who maintain the network by verifying BTC transactions, and adding the blocks to the chain are called MINERS
•Mines receive rewards for adding a full block to the chain and this happens after every 10mins averagely.
•As of today 1st of June 2024, Miners receive 3.125 BTC per block in the BTC Blockchain.
Do not confuse miners and nodes.
Nodes are the people who store maintain ledgers to maintain trust and transparency in the blockchain.
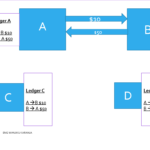
A number of ledgers form a block. Consider the following txns between A and B
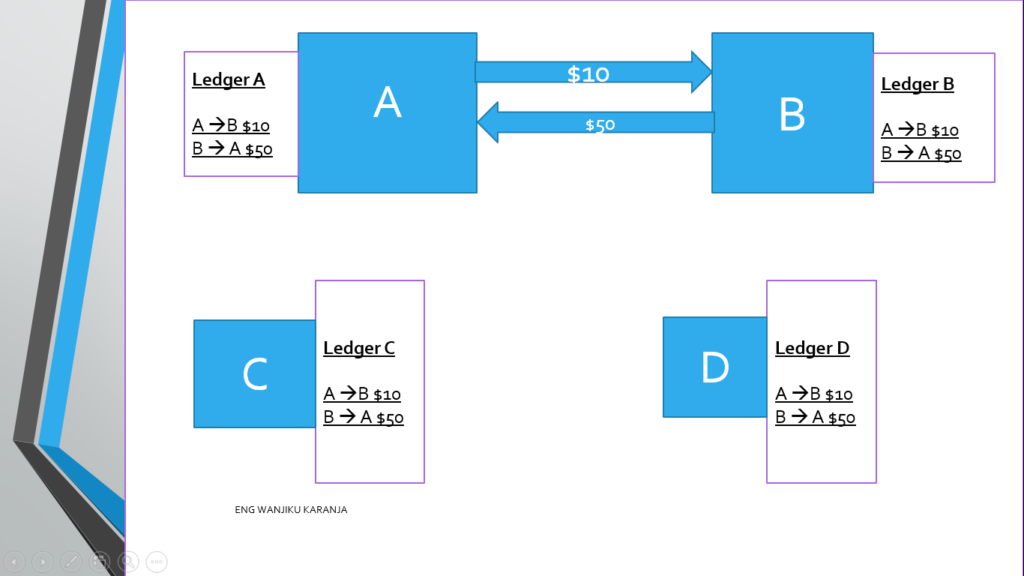
•Every txn will be stored by not only A and B ,but by everyone else C, D, E etc.
This txns is what we are calling a ledger. This ledger will be stored by everyone . ABCD are known as nodes.
•Miners get rewarded for adding blocks in a blockchain. Since the pay is good and everyone would wish to be a miner, a challenge is put out . The first miner to add the block to the blockchain gets the rewards.
•How is the blockchain then secure?
•Remember each block has a hash. And the Hash of the previous block gets saved in the next block.
•If now data is altered in one of the blocks, it will change the hash of that particular block. This will in turn affect the hash of the next block and so on
•From the footprint of evidence, we can now trace where the data was altered from and kick out the miner from that chain of network.
ENG WANJIKU
Views: 36